If in for Loop Break Start Loop Again
Break, Keep, and Else Clauses on Loops in Python
A quick overview of how to write better Python loops
Loops in Python
-
forloop -
whileloop
Let's larn how to use control statements like intermission, continue, and else clauses in the for loop and the while loop.

'for' Statement
The
forstatement is used to iterate over the elements of a sequence (such as a string, tuple, or listing) or any other iterable object. -python docs
for item in iterable:
suite - The iterable is evaluated only once. An iterator is created for the event of that iterable.
- The suite is then executed once for each detail provided by the iterator, in the social club returned past the iterator.
- When the items are exhausted, the loop terminates.
Example 1. 'for' loop
for i in range(one,vi):
print (i)
'''
Output:
1
2
iii
iv
5
''' The for loop may have control statements like pause andgo along, or the else clause.
There may exist a situation in which you may demand to exit a loop completely for a particular condition or you want to skip a part of the loop and offset the next execution. The for loop and while loop have control statements suspension and go along to handle these situations.
'break' Statement
The break statement breaks out of the innermost enclosing for loop.
A break argument executed in the first suite terminates the loop without executing the else clause's suite.
The break statement is used to terminate the execution of the for loop or while loop, and the control goes to the argument after the body of the for loop.
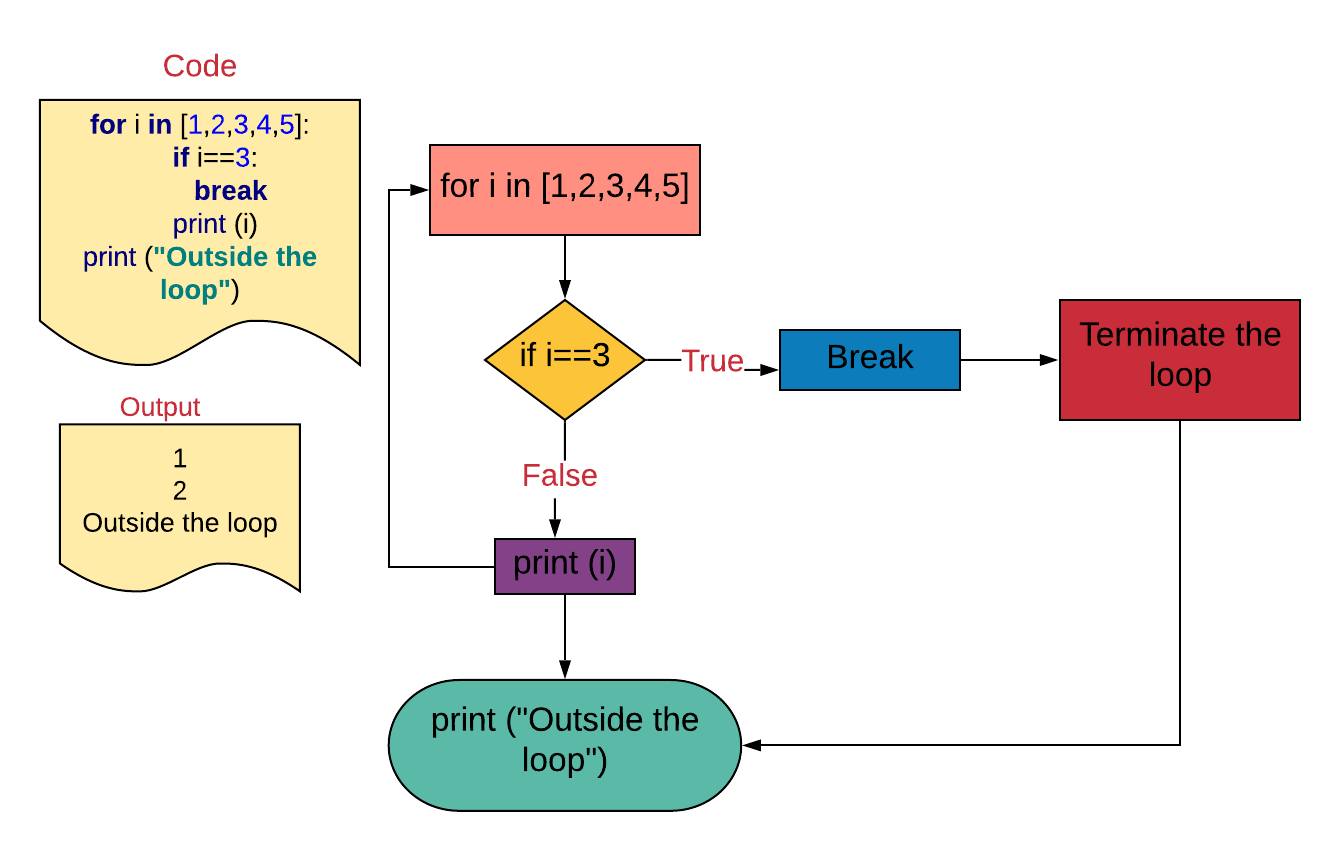
Case 2. Using the 'break' statement in a 'for' loop
- The
forloop volition iterate through the iterable. - If the particular in the iterable is
3, it volition break the loop and the control will go to the statement subsequently theforloop, i.east.,print ("Outside the loop"). - If the item is not equal to
3, it will print the value, and theforloop will proceed until all the items are wearied.
for i in [i,ii,three,iv,5]:
if i==three:
suspension
print (i)
impress ("Outside the loop")
'''
Output:
one
2
Outside the loop
''' Instance 3. Using the 'break' statement in a 'for' loop having an 'else' clause
A break statement executed in the first suite terminates the loop without executing the else clause's suite.

Example:
In the for loop, when the condition i==3 is satisfied, it volition interruption the for loop, and the command will become to the statement after the body of the for loop, i.e., impress ("Outside the for loop").
The else clause is also skipped.
for i in [ane,2,3,iv,5]:
if i==3:
break
impress (i)
else:
print ("for loop is done")print ("Outside the for loop")
'''
Output:
1
2
Outside the for loop
'''
'continue' Statement
The continue argument continues with the side by side iteration of the loop.
A go along statement executed in the first suite skips the remainder of the suite and continues with the next item or with the else clause, if there is no next item.
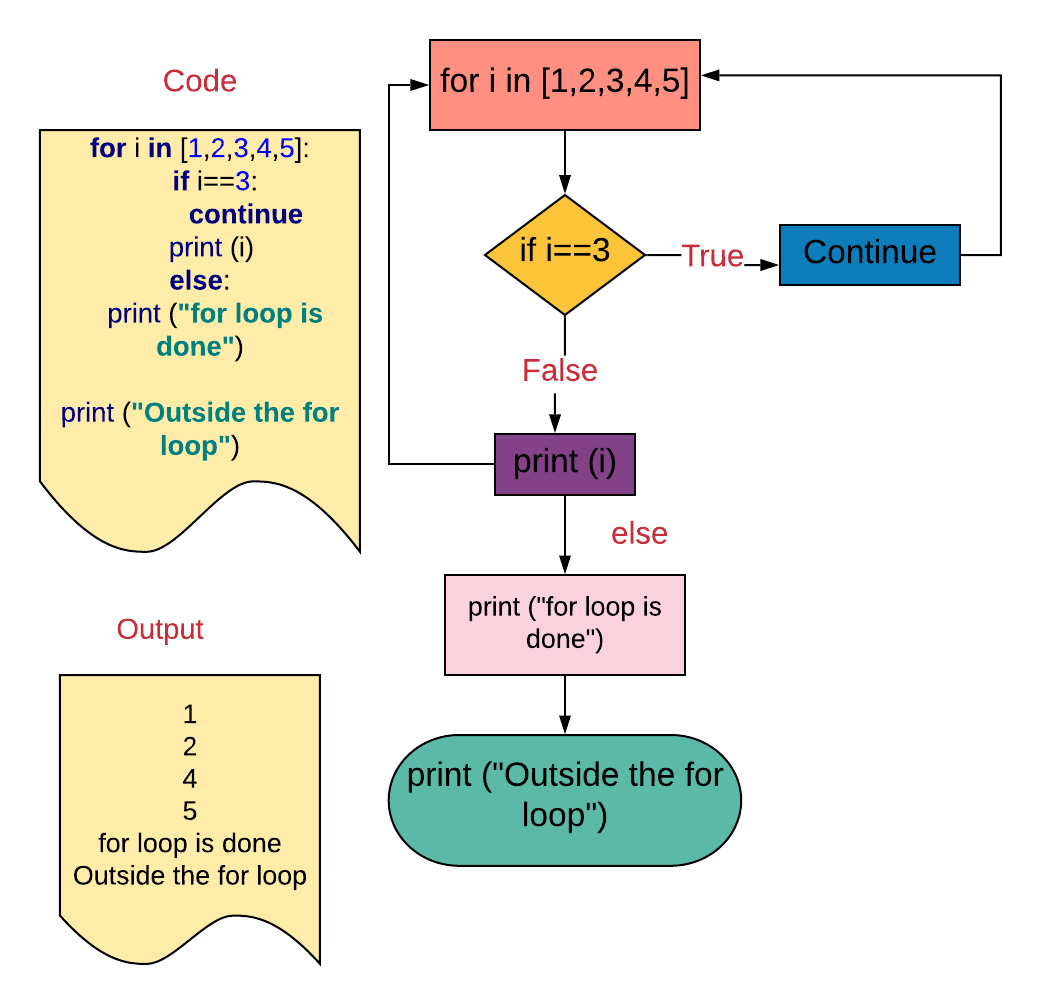
Example 4. Using the 'continue' argument in a 'for' loop
- The
forloop volition iterate through the iterable. - If the particular in the iterable is
3, it volition keep theforloop and won't execute the rest of the suite, i.east.,print (i). - And so element
3volition be skipped. - The
forloop will continue execution from the adjacent element. - The
elseclause is besides executed.
for i in [i,2,3,4,5]:
if i==3:
go on
print (i)
else:
print ("for loop is washed")print ("Outside the for loop")
'''
1
ii
iv
5
for loop is done
Outside the for loop
'''
'else' Clause in 'for' Loop
Loop statements may have an else clause. It is executed when the for loop terminates through exhaustion of the iterable — but not when the loop is terminated by a intermission argument.
Example 5. Using the 'else' clause in a 'for' loop
The else clause is executed when the for loop terminates later the exhaustion of the iterable.
for i in [one,2,3,four,5]:
print (i)
else:
print ("for loop is washed")impress ("Outside the for loop")
'''
1
2
3
4
5
for loop is washed
Outside the for loop
'''
Example half dozen. Using the 'else' clause in a 'for' loop with the 'break' statement
The else clause is not executed when the for loop is terminated past a break statement.
for i in [1,ii,3,iv,5]:
if i==iii:
suspension
print (i)
else:
print ("for loop is done")impress ("Outside the for loop")
'''
1
2
Outside the for loop
'''
Example seven. Using the 'else' clause in a 'for' loop with the 'continue' argument
The else clause is too executed.
for i in [one,2,3,4,v]:
if i==3:
continue
print (i)
else:
impress ("for loop is done")print ("Exterior the for loop")
'''
one
ii
four
5
for loop is done
Outside the for loop
'''
Example viii. Using the 'suspension' statement and 'else' clause in a 'for' loop
Search the particular element in the list. If it exists, break the loop and return the index of the element; else return "Not found."
l1=[i,3,5,vii,9]
def findindex(x,l1):
for alphabetize,particular in enumerate(l1):
if item==10:
render index
break
else:
return "Not institute"impress (findindex(5,l1))
#Output:2print (findindex(10,l1))
#Output:Not found 'while' Loop
The while statement is used for repeated execution as long every bit an expression is true. — python docs
while expression:
suite
else:
suite This repeatedly tests the expression and, if it is true, executes the first suite. If the expression is false (which it may be the first fourth dimension it is tested) the suite of the else clause, if nowadays, is executed and the loop terminates.
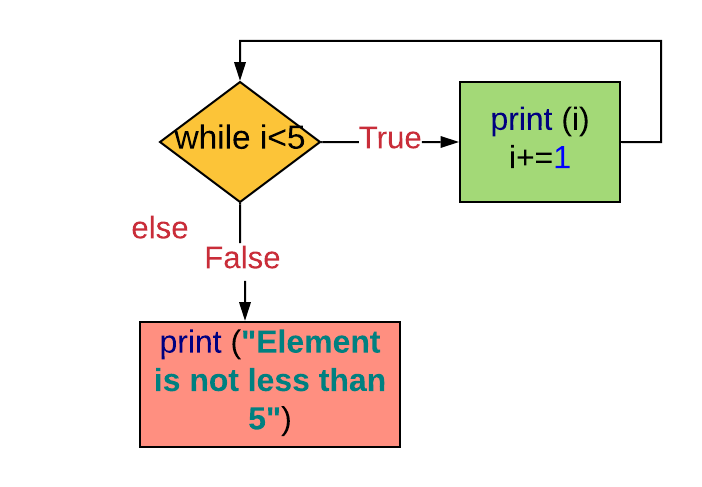
Example 9. Using the 'else' clause in a 'while' loop
The while loop is executed until the condition i<v is False.
The else clause is executed afterward the condition is False.
i=0
while i<5:
print (i)
i+=1
else:
impress ("Element is not less than five") '''
Output:
0
1
ii
3
four
Element is not less than five
'''
'break' Statement
A break statement executed in the first suite terminates the loop without executing the else clause's suite.
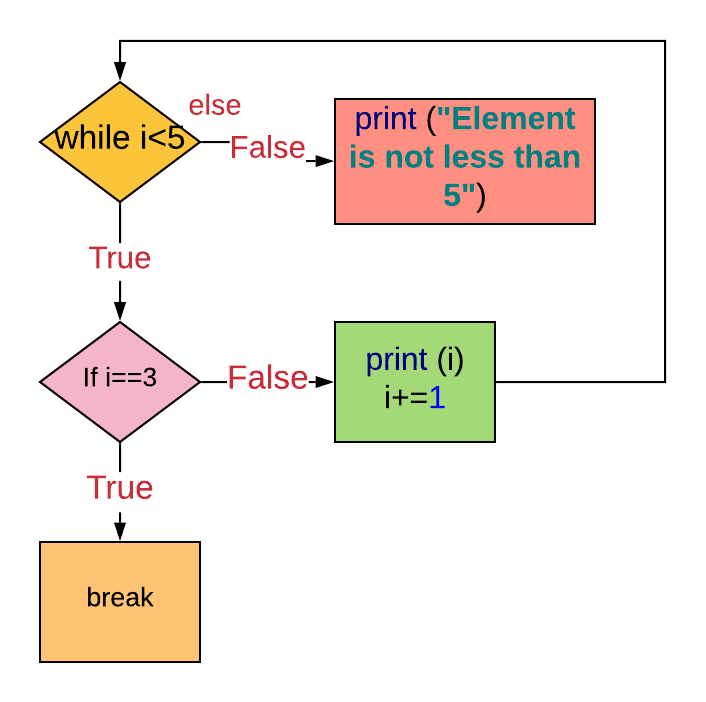
Case 10. Using the 'break' argument and 'else' clause in a 'while' loop
The break statement terminates the loop and the else clause is not executed.
i=0
while i<5:
print (i)
i+=one
if i==3:
break
else:
print ("Element is not less than 5") '''
Output:
0
1
2
'''
'continue' Statement
A go along argument executed in the outset suite skips the residual of the suite and goes back to testing the expression.
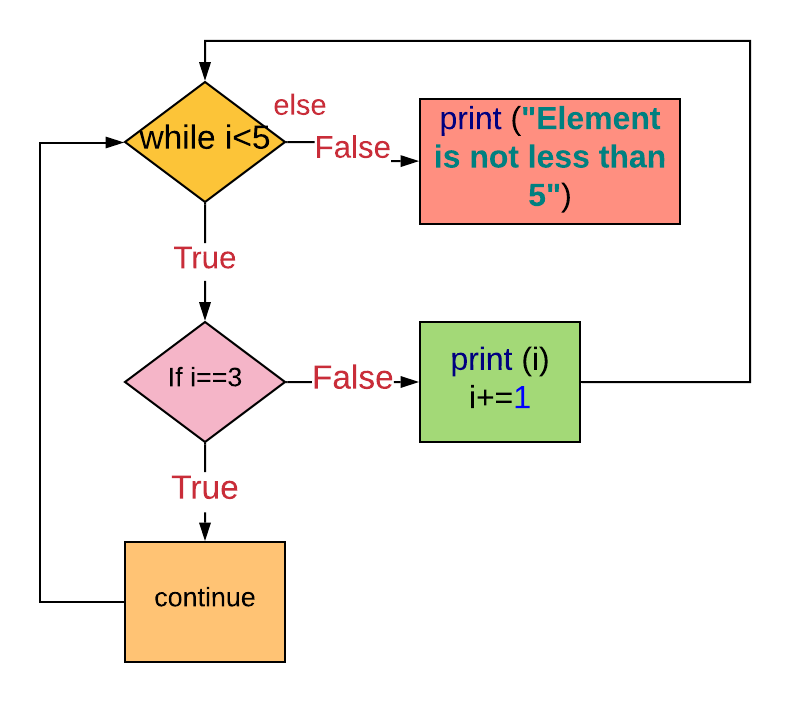
Example 11. Using the 'continue' statement and 'else' clause in a 'while' loop
The go along argument skips the part of the suite when the status i==3 is Truthful. The control goes back to the while loop once again.
The else clause is also executed.
i=0
while i<five:
impress (i)
i+=1
if i==three:
go on
else:
print ("Element is not less than v") '''
Output:
0
1
2
iii
four
Element is non less than 5
'''
Decision
- Python version used is 3.8.i.
- The
intermissionstatement volition stop the loop (bothforandwhile). Theelseclause is non executed. - The
continuestatement will skip the rest of the suite and continue with the next item or with theelseclause, if there is no side by side item. - The
elseclause is executed when theforloop terminates after the exhaustion of the iterable.
Sentry this infinite for more articles on Python and DataScience. If you like to read more of my tutorials, follow me on Medium , LinkedIn , Twitter .
Thank you for reading!
russelllormeaving.blogspot.com
Source: https://betterprogramming.pub/break-continue-and-else-clauses-on-loops-in-python-b4cdb57d12aa
Postar um comentário for "If in for Loop Break Start Loop Again"